What is 6G, or what will 6G be?
6G is the acting name of what will be the sixth generation of cellular technology, with a specific focus on growing the capabilities and lowering the latency of the wireless and edge networks that came with 5G. “Acting name” is the appropriate term to use, as 6G is only a theoretical discussion for now. While many technology companies and governments are discussing what 6G and its infrastructure could look like in the future, most are still working through the wider implementation of 5G infrastructure, leaving 6G in the early research phase.
How is 6G different from 5G?
5G took a giant leap ahead of its 4G predecessor when it hit the stage in the late 2010s 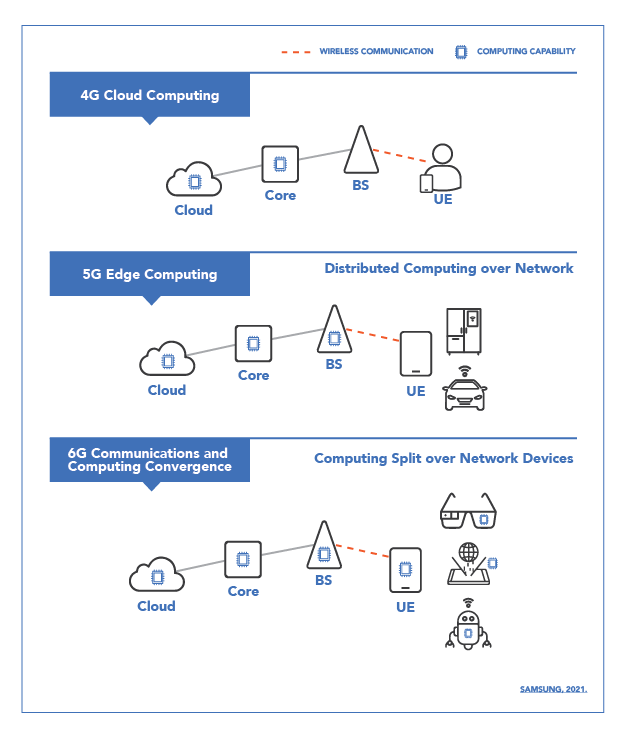
6G is predicted to be a lot like 5G in its general infrastructure, but with even more speed, accuracy, and ubiquity. With 6G’s expected levels of speed and data processing capabilities, many experts believe that more immersive technologies will be possible and will operate in what feels like real time.
More on Edge Computing and IoT: The Future of Edge Computing: Beyond IoT
What makes 6G significant?
There’s no true indication of what 6G will be or what important advancements will come from it, but early predictions indicate that 6G could be as much as 1,000 times faster than 5G. An increase in speed of that magnitude has significant implications, especially in the areas of capacity and speed for data processing. Some examples of how 6G’s predicted bandwidth could expand our existing technological reality include the following:
- Closer to real-time, human-like data processing allows for more immersive experiences and precise operations that weren’t possible in most industries before. The speed and precision that 6G allows could enable more advanced technologies and robotic procedures in industrial use cases like specialized manufacturing, robotic surgery, and robo-military actions.
- 6G will create a negligible amount of lag between queries and data processing needs, which is especially helpful for digital and holographic imagery. With 6G speeds and processing capacity, many experts believe that true-to-form human holograms and XR (extended reality) will become realities.
- 6G is expected to enable technology so powerful that it will have the potential for humans to have small devices installed on their bodies, making it possible for technology-to-brain connections. Experts are calling this possible development “mind computing”.
- Past generations of cellular technology have provided the stage needed for digital sensory experiences, but with the speeds available in 6G, digital sensory experiences are expected to feel like real life.
What could make 6G significant for enterprise networks?
6G brings to life many of the science fiction dreams of past generations, but what will this look like at the enterprise level and in the infrastructure of an enterprise network? Based on current features of the 5G rollout and early expectations for a 6G future, 6G could enable many new opportunities and new areas for caution for enterprises.
AI-Powered Communications
In their forward-looking study into 6G development, Samsung explains that although AI-informed wireless communications are already possible in enterprise networks through 4G and 5G infrastructure, there are limits to this type of communication since 4G and 5G were not created with AI-powered communications in mind. Samsung expects that 6G will be designed with the capacity to meet this communication need and offer “the possibility of embedding AI in various entities comprising wireless networks and services”. This growth in AI-communication capacity will improve enterprise networking features like network planning, energy consumption, and self-healing.
Device-to-Device Data Processing
Data processing happened only on cloud networks in 4G, then on the cloud and on edge devices in 5G. With 6G, it may be possible for 6G-enabled devices to directly transmit requested data to each other, eliminating the bandwidth needed in many cloud and edge device setups; this device-to-device structure could significantly improve the speed of data transmission and further reduce the storage space needed at the network level.
However, a word of caution: much like with the advantages that came with edge devices and networks, there is also the potential disadvantage in increased security breach surfaces. With so many devices processing and sharing data outside of your network’s primary data center, it will be even more crucial that your organization implements strict security parameters and authentication processes around any sensitive data that could be exposed in an open 6G environment.
Infrastructural and Environmental Opportunities
Beyond the everyday actions that happen in your enterprise network, the expansion of 5G and 6G bring several other areas for growth to the table. All of the infrastructural research and implementation going into 5G and 6G will benefit enterprise networks and their topology, or ability to connect and network through more devices around the world, thus opening up greater access for employees and other users who were limited by previous network bandwidth. Tech companies and governments are also looking at ways to redistribute where data and energy are processed, which will likely benefit everyone through a reduced carbon footprint and energy consumption over time.
Read More on Enterprise Networks: Approaches to Cybersecurity in 5G-driven Enterprise Networks
When can we expect to see 6G or something like it?
6G is not expected to roll out on any specific timeline as of yet, but many experts have looked to the rollout timelines for past generations of cellular technologies for their predictions. Since the gap between early research phases and widespread access for past generations has averaged around 10 years, several experts are guessing that 6G will not launch until around 2030. For now, larger technology companies and governments around the world continue to build the massive infrastructural changes needed for full 5G implementation; this infrastructure will set the stage for and simplify the rollout process for 6G when it is ready to launch.
Read Next: Using Wi-Fi 6 and 5G to Build Advanced Wireless Networks



