5G is a next-generation wireless network that promises faster speeds, lower latency, and the ability to connect more devices simultaneously compared to its predecessor, 4G. These improvements are not just incremental; they represent a significant leap forward in wireless technology.
As such, 5G is poised to be a critical component in the ongoing evolution of digital technologies, particularly as artificial intelligence (AI) and the internet of things (IoT) continue to reshape the global tech landscape.
As we stand on the cusp of this new era, it’s essential to not only celebrate the potential benefits of 5G but also to critically examine the challenges and drawbacks associated with its deployment.
Below, we shed light on these topics to help you make an informed decision about making the switch.
Table of Contents
8 issues with 5G networks
There are several issues and disadvantages that necessitate a detailed discussion by telecoms regulators, industry stakeholders, and consumers. These include concerns about network security, the cost of infrastructure development, ecosystem availability, potential health effects, and the risk of exacerbating the digital divide.
Network security
5G networks, like their predecessors, are not immune to security threats. However, the risks are amplified due to the sheer volume of devices that will be connected and the sensitive nature of the data they will handle. Cybersecurity concerns range from data privacy and protection to potential threats to critical infrastructure.
The decentralized nature of 5G networks, with more data being processed at the edge, also opens up new points of vulnerability. Telecom operators and device manufacturers will need to invest significantly in robust security measures to protect against these threats.
The cost of infrastructure development
The transition from 4G to 5G is not a simple upgrade; it requires a complete overhaul of existing infrastructure. This includes the deployment of new antennas and base stations, as well as the installation of high-speed fiber connections to these sites.
The cost of this infrastructure development is substantial and could be a significant barrier to 5G rollout, particularly in rural and remote areas where the return on investment may be lower.
Ecosystem availability
The full potential of 5G can only be realized when a complete ecosystem of 5G-enabled devices and applications is available. This includes not only smartphones but also IoT devices, industrial equipment, autonomous vehicles, and more. The development of this ecosystem is still in its early stages, and it will take time for a wide range of 5G-compatible devices and applications to become available.
Skills and education gap
The deployment and management of 5G networks require a new set of skills. There is a need for professionals who understand not only telecommunications but also cloud computing, cybersecurity, AI, and IoT. This skills gap is a significant challenge and will require investment in education and training to overcome.
Potential health effects
The potential health effects of 5G are a topic of ongoing debate. Some experts have raised concerns about the impact of the higher frequency radio waves used by 5G on human health. However, the FDA, World Health Organization (WHO), and other health organizations have stated that the levels of radiofrequency radiation to which people are exposed from 5G are below the limits set by international guidelines and are not expected to have health effects.
Potential interference with flight operations
There have been concerns raised about the potential for 5G signals to interfere with radio altimeters in aircraft, which measure the height of the aircraft above the ground. The issue arises because the frequency band, the 3.5 GHz range, used by 5G is close to that used by radio altimeters, which use the 4.2 to 4.4 GHz band.
In January 2022, several international airlines had to suspend flights to the United States as 5G was deployed across several airports in the country. While telecom operators and 5G equipment manufacturers assert that the risk of interference is low, the FAA continues to monitor and issue guidelines as more information becomes available.
Battery drain on cellular devices
5G networks offer faster speeds and lower latency, but these benefits come at the cost of higher power consumption. This could lead to faster battery drainage in 5G-enabled devices, particularly when downloading or streaming large amounts of data.
Device manufacturers will need to find ways to improve battery life to ensure that users can enjoy the benefits of 5G without constantly worrying about their battery level. For the time being, companies like Samsung are advising customers to use the “Optimize battery usage” settings.
Risk of exacerbating the digital divide
While 5G has the potential to revolutionize many aspects of our lives, there is a risk that it could exacerbate the digital divide. The high cost of 5G infrastructure development could lead to a situation where 5G is only available in urban and affluent areas, leaving rural and low-income communities behind. Policymakers and telecom operators will need to work together to ensure that the benefits of 5G are accessible to all.
What are the advantages of 5G?
Despite the issues associated with 5G, the transformative potential of the technology is manifold. From lightning-fast download speeds to enabling a new generation of IoT devices, 5G has a lot to offer.
Increased speed
One of the most touted benefits of 5G is its speed. 5G networks are expected to deliver data rates of up to 10 Gbps, which is up to 100 times faster than 4G LTE. That means you could download a full-length HD movie in a matter of seconds on a 5G network, compared to several minutes on a 4G network.
This increased speed will not only improve the user experience for data-intensive applications such as video streaming and gaming but also open up new possibilities for applications such as virtual reality and augmented reality (VR and AR).
Lower latency
Latency, or the delay before a transfer of data begins following an instruction for its transfer, is expected to be in the range of 1 millisecond or less in 5G networks, compared to around 20-70 milliseconds in 4G networks. This near real-time communication will be critical for applications where immediate response is necessary, such as autonomous vehicles, remote surgery, and esports.
Greater capacity
5G networks will have a much greater capacity than 4G networks. This means they will be able to handle more devices, from smartphones and tablets to IoT devices and sensors, without slowing down. This will be particularly important in urban areas and at large events where many people are trying to connect to the network at the same time.
Improved efficiency
5G networks are designed to be more efficient than 4G networks. They use advanced technologies such as network slicing, which allows operators to create multiple virtual networks within a single physical 5G network. This means that network resources can be allocated more efficiently, ensuring that each user gets the level of service they need.
Enabling new technologies
Perhaps the most exciting aspect of 5G is its potential to enable new technologies and applications. The combination of high speed, low latency, and high capacity makes 5G a key enabler for technologies such as IoT, autonomous vehicles, smart cities, and Industry 4.0. With 5G, we could see everything from remote surgery and autonomous vehicles to a new generation of smart homes and factories.
5G network trends
The landscape of 5G networks is evolving rapidly, with new devices, applications, and use cases emerging on a regular basis. Here are some of the key trends shaping the 5G ecosystem.
Growth in 5G devices
According to the GSA 5G-Ecosystem May 2023 Summary Report, the number of announced 5G devices increased by 2.4% between March and April 2023, reaching a total of 1,942 devices.
Of these, 1,557 are commercially available, representing 80.1% of all announced 5G devices. This is a significant increase of 51.4% in the number of commercial 5G devices since the end of April 2022.
This steady growth in the number of commercially available devices is expected to continue, providing consumers with a wider range of options for accessing 5G networks.
Rapid network expansion
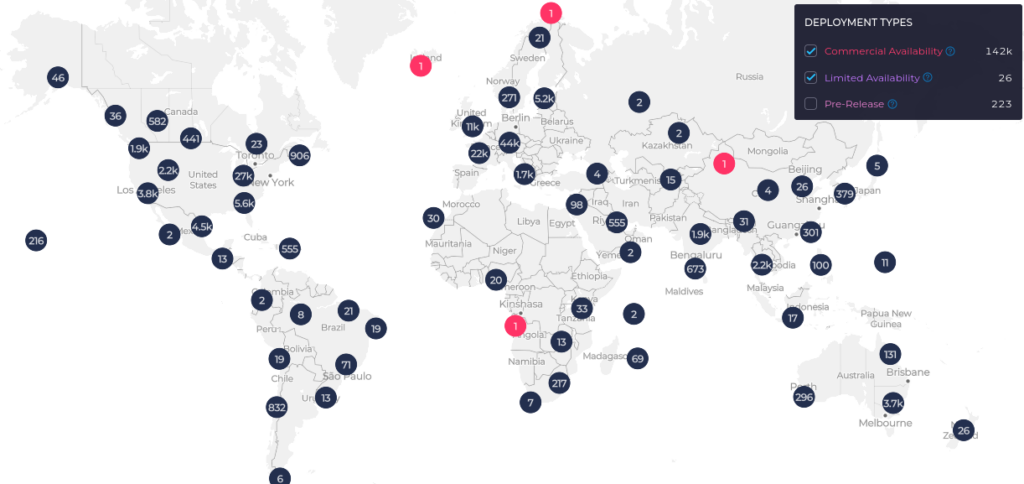
The OOKLA 5G Map™ tracks the rollout of 5G in cities around the world. By observing the progress of 5G over a couple of weeks, it’s easy to see the frenetic pace with which telecom providers are moving to make 5G available. At the time of publishing, there were approximately 142,000 sites with commercial 5G availability on five continents.
Enterprise adoption and private 5G networks
The 5G Thematic Intelligence Report 2023 published by Research and Markets suggests that enterprises will increasingly look at wireless connectivity for branch offices in the more fluid hybrid work environment.
Private 5G, in particular, is positioned as a complement to in-building Wi-Fi networks that, along with edge computing, will enable applications such as AR, VR, video analytics, and autonomous robots.
Consumer demand and concerns
A survey titled “5G and the Future” by semiconductor firm Arm established that the number of 5G subscriptions is growing by 1 million per day, while the number of providers offering 5G service deployments surpasses 130,000 worldwide. Industrial and commercial customers have also launched trials and early commercial deployments with private 5G networks.
The survey highlighted strong demand for 5G, with half the respondents predicting 5G products and services would constitute 51% to 75% of their telecommunications sales by 2027. However, it also revealed concerns about energy consumption and high upfront costs.
Open RAN and cloud-based infrastructure
The Arm survey also indicated that Open RAN and cloud-based infrastructure are expected to gain traction quickly. Just over 40% of respondents believe Open RAN will constitute half of all equipment shipments by 2025. Meanwhile, 53% predicted clouds would host 51%-75% of 5G infrastructure by 2027. However, 44% said quality-of-service remains the largest potential stumbling block for cloudified 5G.
These trends highlight the dynamic nature of the 5G ecosystem and the opportunities and challenges that lie ahead as this technology continues to evolve.
Future issues in 5G networks
As 5G continues to evolve and become more widespread, new challenges are likely to emerge. Here are some potential future issues that stakeholders should be aware of:
Network congestion
While 5G networks are designed to handle a much larger volume of data and devices than their predecessors, the rapid growth in the number of connected devices could still lead to network congestion. This could result in slower speeds and reduced performance, particularly in densely populated urban areas.
Cybersecurity threats
As more devices become connected to 5G networks, the potential for cybersecurity threats will increase. These could include data breaches, identity theft, and attacks on critical infrastructure. The industry will need to stay ahead of these threats by investing in robust security measures and continually updating and improving them.
Regulatory challenges
The deployment of 5G networks also presents regulatory challenges. These include issues related to spectrum allocation, data privacy, and health and safety. Regulators will need to balance the need for innovation and growth with the need to protect consumers and maintain the integrity of the network.
Technological obsolescence
As technology continues to evolve at a rapid pace, there is a risk that 5G networks could become obsolete before they are fully deployed. This could result in wasted investment and a need for further upgrades.
Can 5G make you sick?
One of the more controversial topics surrounding 5G is its potential impact on health. While earlier claims that 5G might weaken the immune system or even cause viruses have been roundly debunked, some concerns persist about cancer risks posed by long-term radiation exposure.
However, the FDA, WHO, and other health research and advisory organizations have stated that the levels of radiofrequency radiation to which people are exposed from 5G are below the limits set by international guidelines and are not expected to have health effects.
Bottom line: Transitioning to 5G in the enterprise and worldwide
As we stand on the precipice of a new era in telecommunications, the transition to 5G networks presents a complex tapestry of opportunities and challenges.
The promise of 5G is undeniable — with its increased speed, lower latency, and greater capacity, it has the potential to revolutionize not only how we communicate but also how we live and work. It is a key enabler for a host of emerging technologies, from IoT and autonomous vehicles to smart cities and Industry 4.0.
However, the journey to 5G is not without its hurdles. Concerns about network security, the cost of infrastructure development, and the risk of exacerbating the digital divide are all valid and require careful consideration. Moreover, the rapid pace of technological change means that new challenges are likely to emerge as 5G networks become more widespread.
Considering implementing a private 5G network in your organization? Here’s a guide to the best 5G network providers for business.



