Software-Defined Wide Area Network (SD-WAN) providers and vendors give enterprises the power to mold and manage their networks through software-defined intelligence, and offer enhanced security features and simplified network management. They should be the staple for businesses seeking a more efficient and cost-effective network solution.
If you’re considering adding SD-WAN to your network infrastructure, here is our pick for the top seven SD-WAN providers and vendors in 2023:
- Aryaka: Best for global WAN (Read more)
- Citrix: Best for hybrid cloud (Read more)
- Versa Networks: Best for fast-growing businesses (Read more)
- HPE Aruba Networking: Best for zero-trust integration (Read more)
- Fortinet: Best for scalability (Read more)
- VMware: Best for users with multiple virtual machines (Read more)
- Cisco Meraki SD-WAN: Best for advanced security (Read more)
Featured Network Monitoring Software
Top SD-WAN software comparison table
Below is a table summarizing the core features found in SD-WAN software.
| Supports traditional routing | Real-time threat intelligence | End-to-end secure architecture | ZTNA | Starting price | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aryaka | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✘ | Contact vendor for a quote |
| Citrix | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | Contact vendor for a quote |
| Versa Networks | ✘ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | Contact vendor for a quote |
| HPE Aruba | ✘ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | Contact vendor for a quote |
| Fortinet | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | Contact vendor for a quote |
| VMware | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✘ | Contact vendor for a quote |
| Cisco Meraki | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✘ | Contact vendor for a quote |
Jump to:
- Key features of SD-WAN software
- How to choose the best SD-WAN software for your business
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Methodology
Aryaka
Best for global WAN
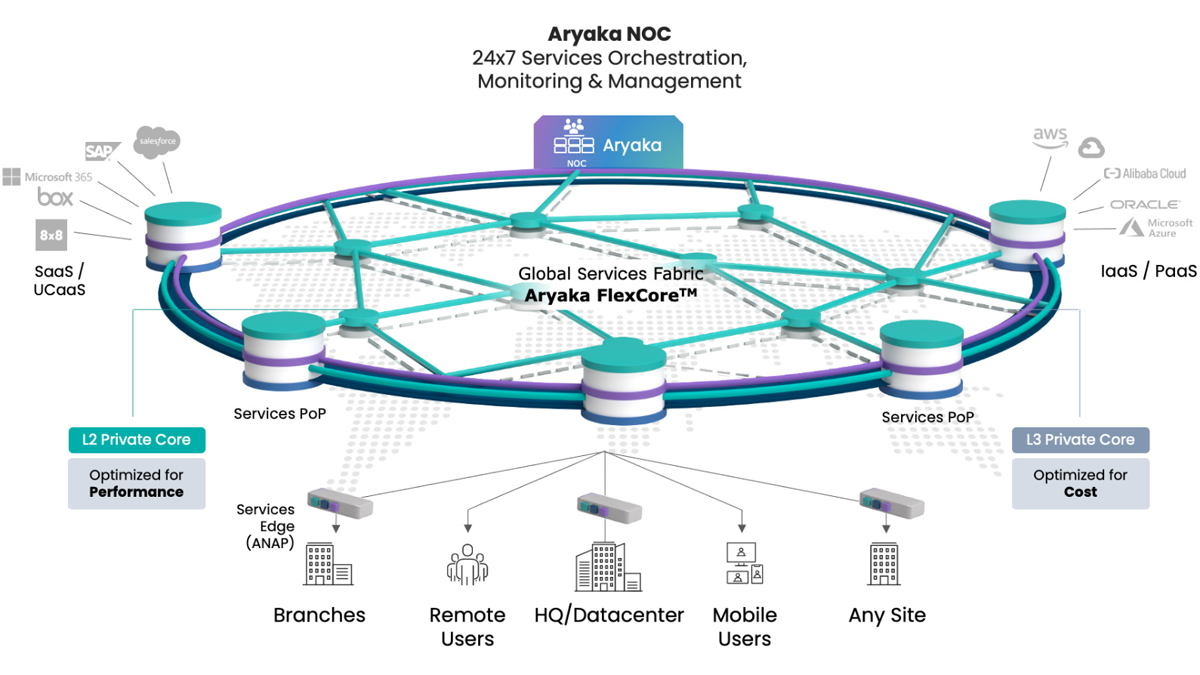
Aryaka is a cloud-based SD-WAN solution that provides connectivity and application delivery to global WANs. The solution offers a centralized management console to enable users to monitor and make changes to their global network. The central management is powered by SmartConnect, a network optimization feature that helps users have end-to-end visibility and control over all their application and network segments.
Aryaka uses a FlexCore network to provide enterprises with an adaptable Network-as-a-Service, which enables them to connect sites, users, and clouds anywhere in the world. Some of its network security capabilities include URL filtering, malware blocking, content filtering, and cloud optimization.
Pricing
Contact the vendor for a quote.
Features
- The platform inter-connects enterprise sites, hybrid workers, and cloud workloads.
- Eliminates service and support issues where a telco or regular managed service provider (MSP) relies on technology from a third party.
- The middle mile’s Layer 2 over fiber architecture avoids ISP peering issues and drives high performance.
- 24/7 service orchestration, monitoring, and management.
Pros
- Easy to implement and low learning curve.
- Fast support response time.
- End-to-end visibility.
- Offers centralized management feature.
- Excellent technical support.
Cons
- Some users say the solution is somewhat expensive.
- Management portal can be improved.
- There is no transparent pricing plan nor free trial.

Citrix
Best for hybrid cloud
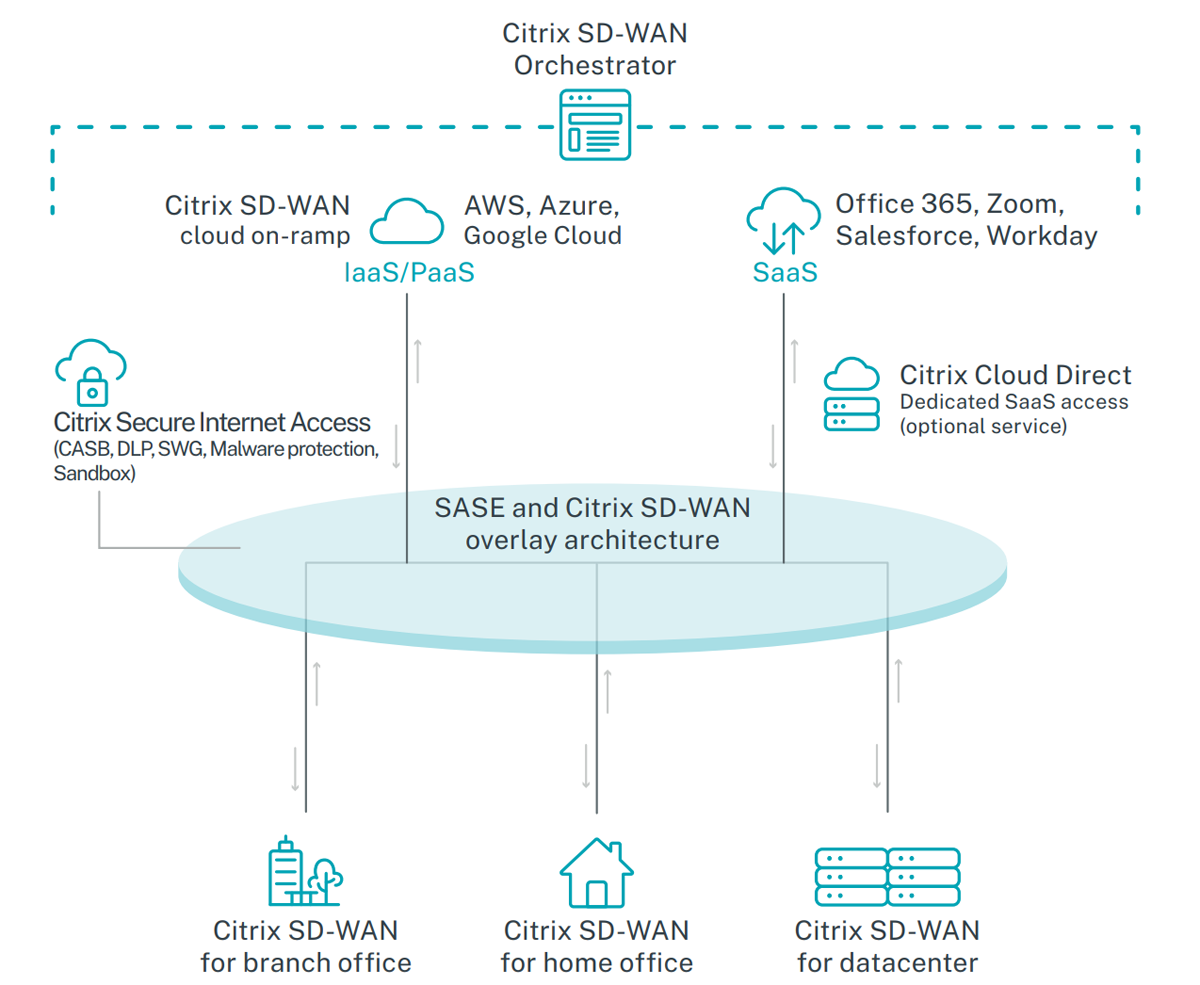
Citrix is most suitable for enterprises running a hybrid multicloud approach as it provides them with a simplified way to optimize applications and automate connectivity. The solution offers a single cloud-based user interface to facilitate WAN management and ensure users can implement and see security policies across their network.
Citrix SD-WAN comes as a key networking capability of the Citrix Secure Access Service Edge (SASE) architecture approach, which gives the flexibility to choose whether security capabilities are enabled on-premise or in the cloud. With the platform, admins can manage and receive alerts about potential threats and also give access to only those they trust to avoid unnecessary disruptions.
Pricing
Contact vendor for pricing.
Features
- Remote access/control capability.
- Congestion management functionality (detection, avoidance, and remediation).
- Multi-cloud connectivity (Azure, AWS, and GCP).
- Remote monitoring and management.
- Zero-touch provisioning.
Pros
- Easy to learn and use.
- Citrix SD-WAN can optimize application performance and automate connectivity for all users wherever they are.
- Centralized policy management.
- It has packet loss concealment functionality.
Cons
- The standard edition lacks WAN optimization capability.
- Limited customization.
- No transparent pricing.

Versa Networks
Best for fast-growing businesses
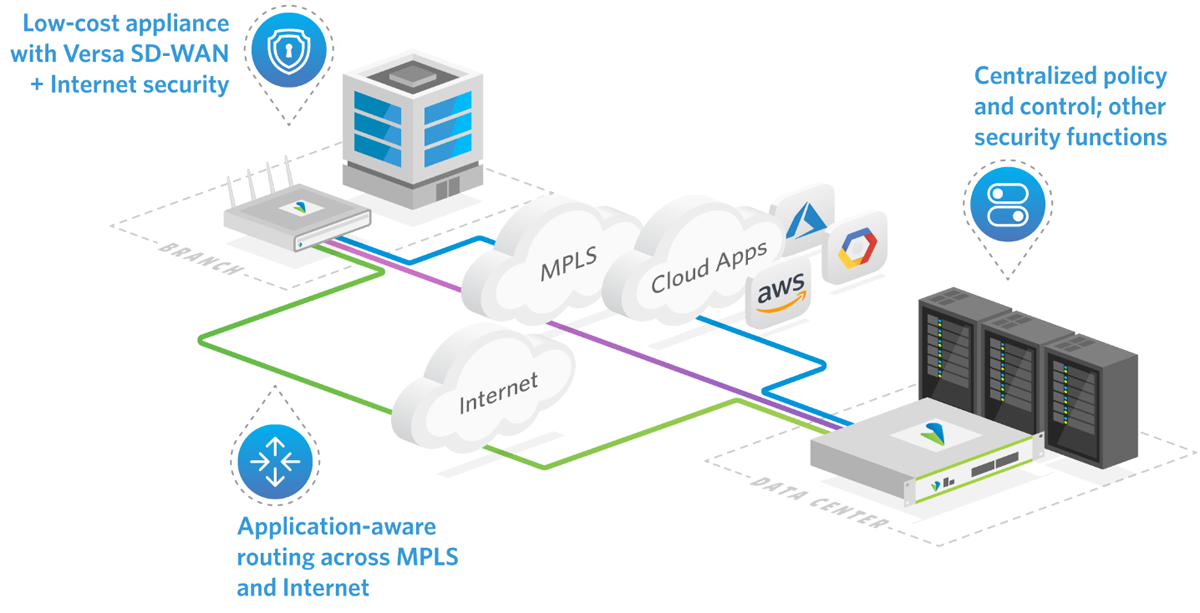
Versa Networks helps secure and simplify modern networks for enterprises, small businesses, and end users. The solution offers an AI/ML-powered single-vendor Unified SASE that integrates services via the cloud, on-premises, or hybrid.
Versa can be managed through a unified console and delivers SASE services such as Secure SD-WAN, Next-Generation Firewall, Next-Generation Firewall-as-a-Service, Cloud Network Firewall, Unified Threat Management (UTM) including Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA), Data Loss Prevention (DLP), Remote Browser Isolation (RBI), and User and Entity Behavior Analytics (UEBA).
This approach makes Versa a comprehensive tool for businesses, not only for network optimization and security but also for advanced network analytics.
Pricing
Contact Versa’s sales team for pricing.
Features
- Deployable on-premise or in a cloud or hybrid environment.
- Ability to identify traffic flows to SaaS applications such as Office 365, Salesforce, or Gmail.
- Offers sub-second packet steering across multiple WAN interfaces.
- Packet loss reduction capability through services such as FEC and packet replication.
- Powered by AI/ML.
Pros
- Single management interface.
- Easy to learn and use.
- Centralized policy and control.
- It can be deployed in the cloud, on-premises, or hybrid.
- Easy to navigate.
Cons
- The GUI analytics feature can be improved.
- Documentation resources can be improved.
- No pricing information.

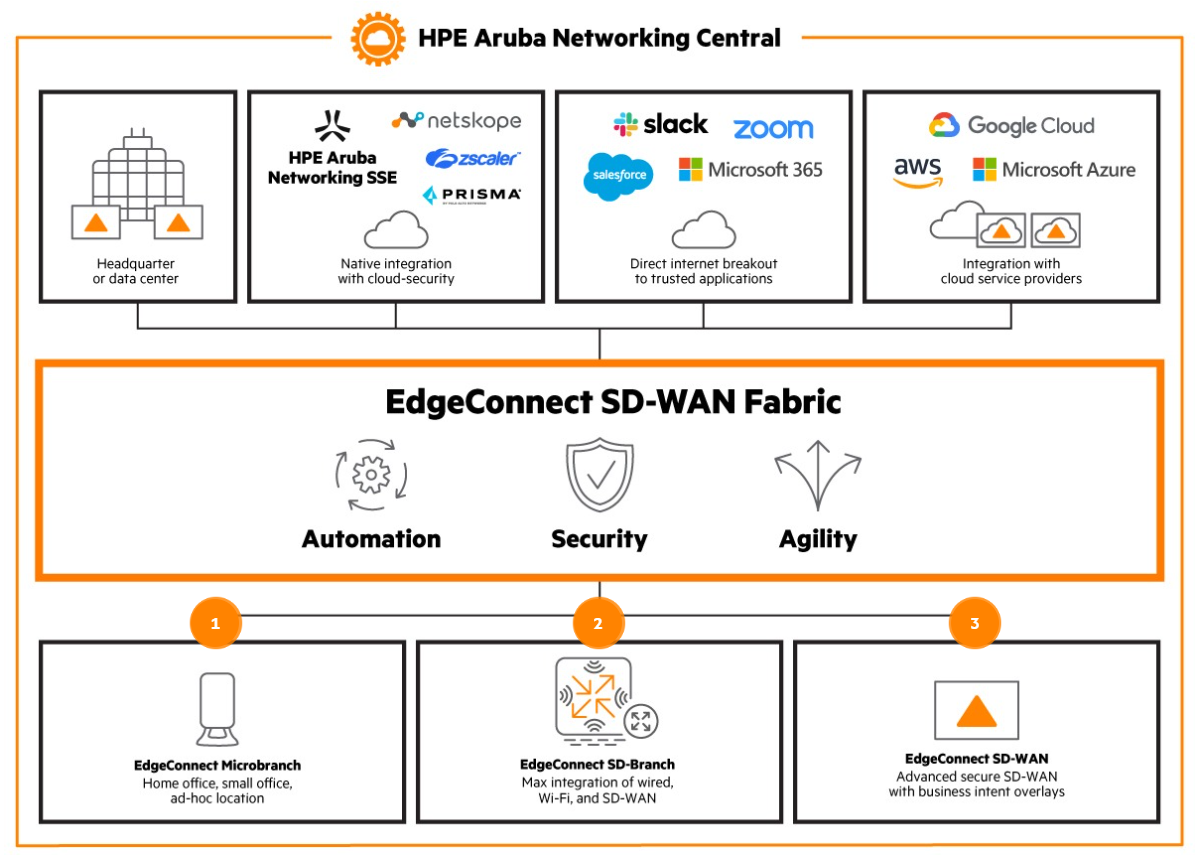
HPE Aruba Networking
Best for zero-trust integration
Formerly known as Silver Peak, HPE Aruba focuses on providing a secure access services edge (SASE) that powers WAN, branch, and edge security. It enables application performance, security, and routing that are dictated by top-down business policies, not bottom-up technology constraints.
With HPE Aruba, users can enforce end-to-end security policies across their enterprise, as well as have access to manage their SD-WAN, firewall, and routing and optimize their WAN on a central management system. There is also a zero-trust security capability designed to protect against threats and secure remote access and sensitive data in SaaS applications.
Pricing
Contact the vendor for a quote.
Features
- Centralized orchestration simplifies the implementation of changes.
- Automates real-time response.
- Unifies SD-WAN, firewall, WAN optimization, and application.
- Supports zero-trust capabilities.
Pros
- Businesses can connect to the cloud with a single SD-WAN fabric.
- Offers fast troubleshooting.
- WAN acceleration.
- Zero-trust security capability for remote access management.
Cons
- Poor documentation.
- There is no pricing information.
- Absence of free trial.

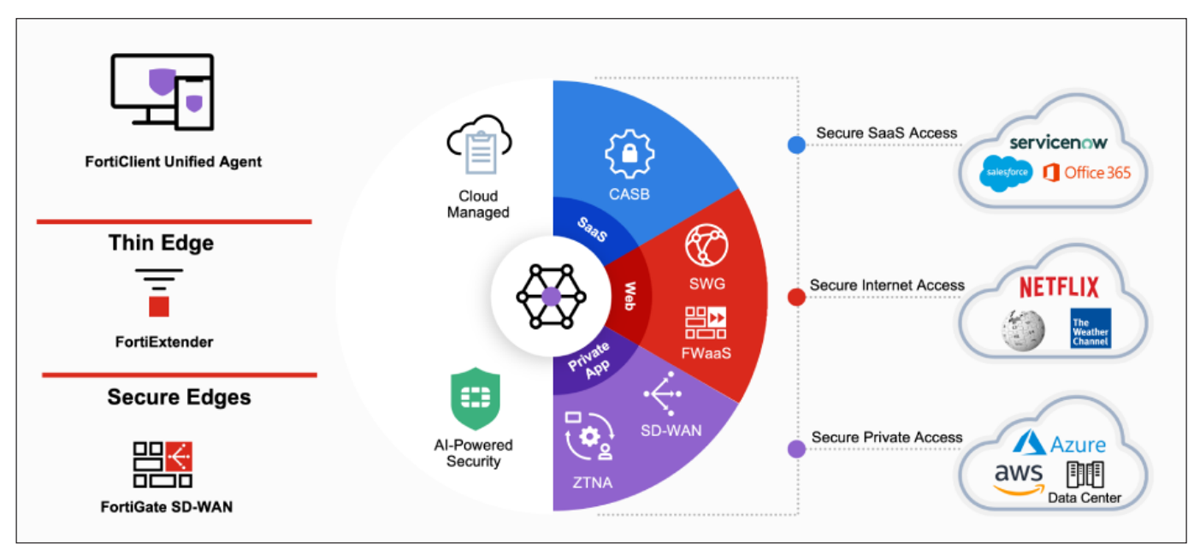
Fortinet
Best for scalability
Fortinet Secure SD-WAN delivers a fast, scalable, and flexible SD-WAN. With a security-driven networking approach, it consolidates SD-WAN, next-generation firewall (NGFW), and advanced routing into one suite.
Key features include NOC operations, a central management functionality that can manage over 100,000 devices, including switches, firewalls, LTE/5G, and access points. There is also FortiGuard, which provides real-time insights, detection, and prevention against known and unknown vulnerabilities in applications and devices.
Pricing
Contact the vendor for a quote.
Features
- Deep packet inspection (DPI).
- Orchestrate consistent network and security policies.
- Application-aware traffic control.
- WAN and security are powered by one operating system (FortiOS).
- One management console covers SD-WAN.
- Unified Threat Protection license.
Pros
- Scalable to up to 100,000 devices.
- Offers real-time insights.
- Advanced visibility with AI.
- It can be managed from a central console.
- Offers zero-trust security.
Cons
- It may not be suitable for smaller businesses.
- FortiManager for central device management is priced separately.

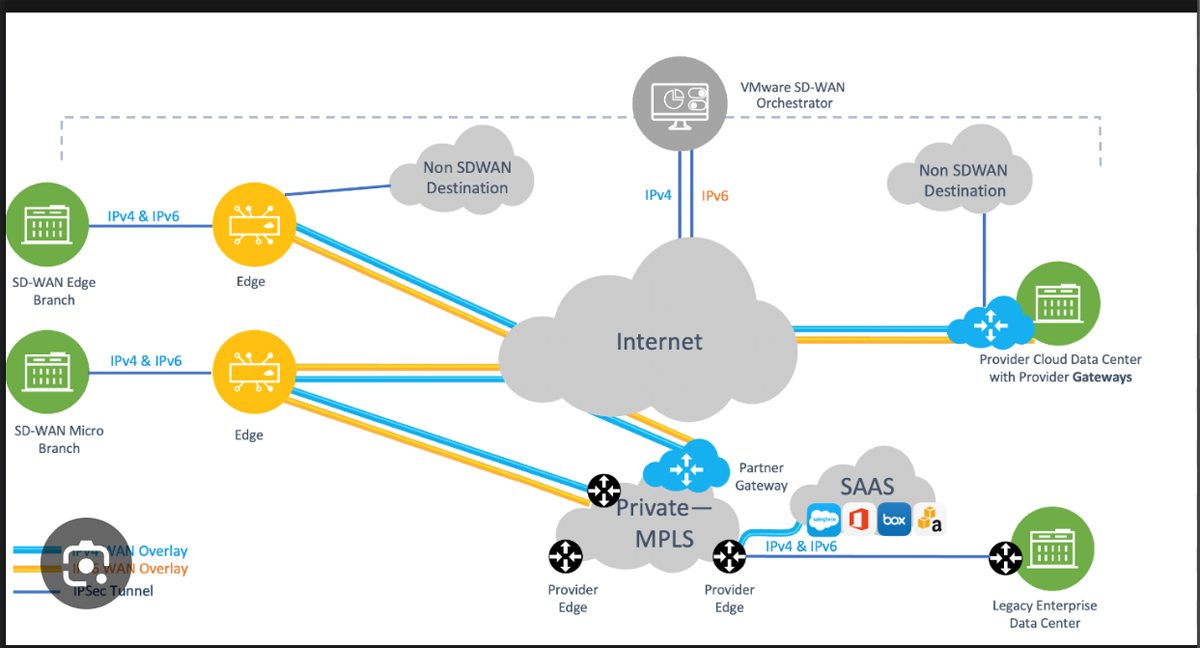
VMware
Best for users with multiple virtual machines (VMs)
VMware SD-WAN evolved from its acquisition of VeloCloud. It leverages cloud hosting to simplify the deployment and management of network devices and employs traffic steering to applications in the data center and the cloud. It combines the bandwidth of broadband with existing WAN connections to connect users to data centers and cloud-based applications from any location in the network.
VMware enables businesses to use more applications using fewer physical servers because it requires less space in your data center while using less energy and power. It allows multiple VMs to be connected to the same host computer.
Pricing
Contact the vendor for a quote.
Features
- Optimizes traffic over multiple available connections.
- Cloud-based management allows ubiquitous access across all devices.
- Dynamic steering of all traffic for optimized application and data delivery.
- Configurations are pushed from the central orchestrator to the edge device.
Pros
- Optimizes direct path to public and private clouds.
- Fast and solution-oriented work.
- Supports most OSs.
- It offers zero-touch branch deployment.
Cons
- License cost.
- Limited documentation.
- Lacks intuitive user interface.

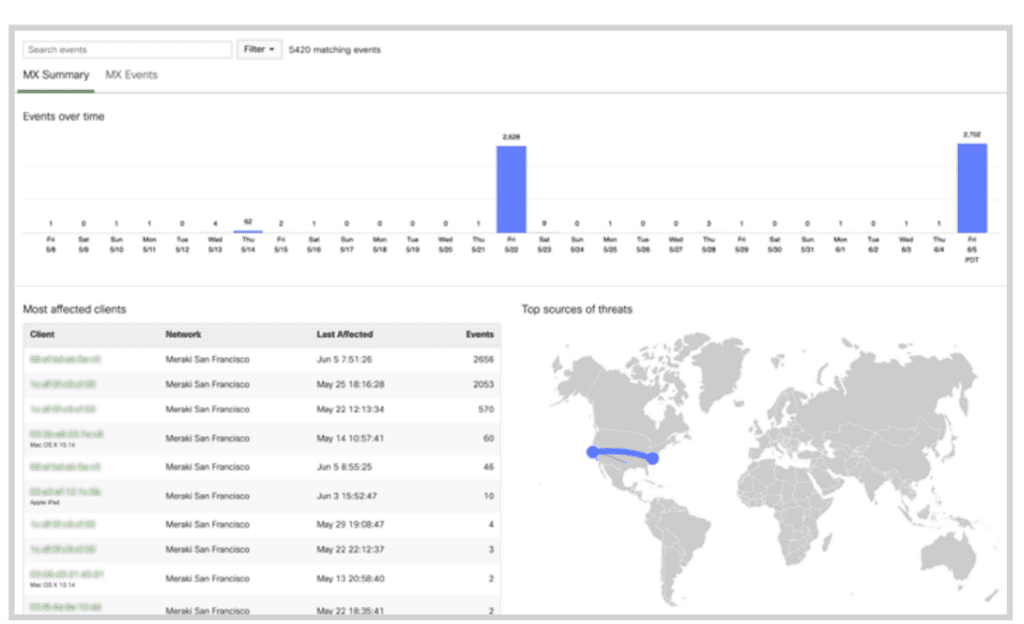
Cisco Meraki SD-WAN
Best for advanced security
Cisco SD-WAN powered by Meraki is delivered through Meraki MX appliances. With two or more appliances, users can establish Auto VPN tunnels over any WAN link between devices and locations.
For adequate security, Cisco SD-WAN offers natively integrated security, encompassing layer-7 firewall, Cisco AMP with Threat Grid, Cisco SNORT IDS/IPS, Cisco Umbrella SIG for cloud security, and content filtering.
The solution also offers advanced analytics and insights into key factors that affect the performance of VPN tunnels. Some of the factors monitored through a central dashboard include packet loss, jitter, and latency. Cisco SD-WAN also comes with a real-time performance telemetry that enables autonomous decision-making regarding the selection of the most suitable path for meeting the performance requirements of essential cloud applications and Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) services.
Pricing
Contact the vendor for a quote.
Features
- Virtual MX is a virtual instance of Meraki security.
- Layer-7 firewall.
- Zero-touch provisioning.
- Extends SD-WAN to public cloud environments for optimized areas.
Pros
- Supports content filtering.
- Allows lots of customization.
- Advanced monitoring and analytic features.
- Visibility into network activities through a single dashboard.
Cons
- Some users complain about limited logging features for the firewall.
- No pricing details.
- No command-line interface.
Key features of SD-WAN software
Most SD-WAN solutions include features such as dynamic path selection, application-based routing, and security integration, as well as promoting cost efficiency.
Dynamic path selection
SD-WAN utilizes multiple paths, such as Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS), broadband, 4G/5G, and even satellite connections, to transmit data. This reduces the chances of network outages or congestion that businesses experience.
This dynamic path selection ensures continuous connectivity and minimizes downtime. If one path experiences issues, traffic can seamlessly shift to an alternative path, improving network reliability.
Application-based routing
SD-WAN offers intelligent routing based on application awareness. This means that it can identify and prioritize traffic based on the specific needs of applications. Critical applications like VoIP or videoconferencing can be given higher priority, ensuring a consistent and high-quality user experience.
This dynamic routing ensures that network resources are allocated where they are needed most, optimizing performance and reducing latency.
Cost efficiency
Though SD-WAN solutions require an initial investment, they often lead to significant cost savings over time. Businesses gain in savings over time because SD-WAN can optimize network resources, reduce downtime, and enable the use of cost-effective internet connections alongside expensive MPLS links.
Security integration
Network security is a paramount concern for businesses in the digital age. SD-WAN incorporates advanced security features that help protect the network from threats. These features may include next-generation firewalls, intrusion detection and prevention systems, and encryption protocols.
With these levels of security integrations, businesses can reduce the complexity of their network architecture and enhance their overall security posture.
Visibility and analytics
SD-WAN provides detailed insights into network performance through advanced analytics and reporting tools. Network administrators can monitor traffic in real-time, identify bottlenecks, and diagnose issues quickly.
This level of visibility allows for proactive network management, capacity planning, and troubleshooting, ultimately leading to improved network performance and reliability.
How to choose the best SD-WAN software for your business
When shopping for the best SD-WAN provider, it’s best to have a list of your enterprise’s particular SD-WAN requirements. While the end goal of most SD-WAN providers is the same, some solutions are more robust and efficient than others.
Here are steps you can follow to select the best SD-WAN provider for your business:
- Define your goals and requirements.
- Conduct your research about various SD-WAN providers.
- Narrow your list down to the top three that align with your needs.
- Request a demo and trial of the platform to better understand it.
- Consider costs to ensure the tool you select is within your budget.
- Vendor reputation is also an important consideration. Read users’ feedback from review sites to learn about users’ experiences, ease of use, and the general usability of the platform.
- Select the best tool that meets your criteria.
These steps can help you select the best SD-WAN provider for your needs. Our research found that Versa is ideal for fast-growing businesses looking for a scalable tool. Large enterprises may find VMware, Cisco Meraki, and Fortinet beneficial, while businesses with multiple locations and distributed teams will benefit from Citrix, HPE Aruba, and Aryaka’s capabilities.
But it’s important to do your own research and ensure you are implementing a solution that works for your unique use case.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How secure is SD-WAN?
The security of SD-WAN depends on the specific implementation and security measures in place, but it can be made secure with proper configurations and additional security solutions.
Is SD-WAN better than MPLS?
SD-WAN can be better than MPLS for many organizations due to its cost-effectiveness, flexibility, and ability to optimize traffic over multiple network connections.
What is the main difference between software-defined networking (SDN) and SD-WAN?
The main difference between software-defined networking (SDN) and SD-WAN is that SDN is a broader networking approach that centralizes network management and control, while SD-WAN focuses more on optimizing and managing wide-area networks.
Methodology
We analyzed several SD-WAN providers and selected the best options based on five parameters: core features and functionalities, ease of use, support/customer service, cost/pricing, and scalability/flexibility.
We gathered primary data about each platform from the vendor’s website, data sheets, whitepapers, and documentation. We also reviewed users’ feedback on review sites to learn about current and past users’ experiences. This information helped to balance our view on each product.
Bottom line: SD-WAN advantages in the enterprise
Given how network performance can impact business success, deploying SD-WAN is a strategic advantage for organizations seeking to stay competitive and meet the demands of the modern business environment. SD-WAN has the ability to transform your organization’s network connectivity by optimizing the direction of traffic on the network via dynamic path selection. Its advanced features can also help organizations maintain greater agility, network reliability, and security on their network infrastructure.
Improve the security of your network with one of the top network access control solutions to keep out unwanted traffic.





